By Joan Leotta

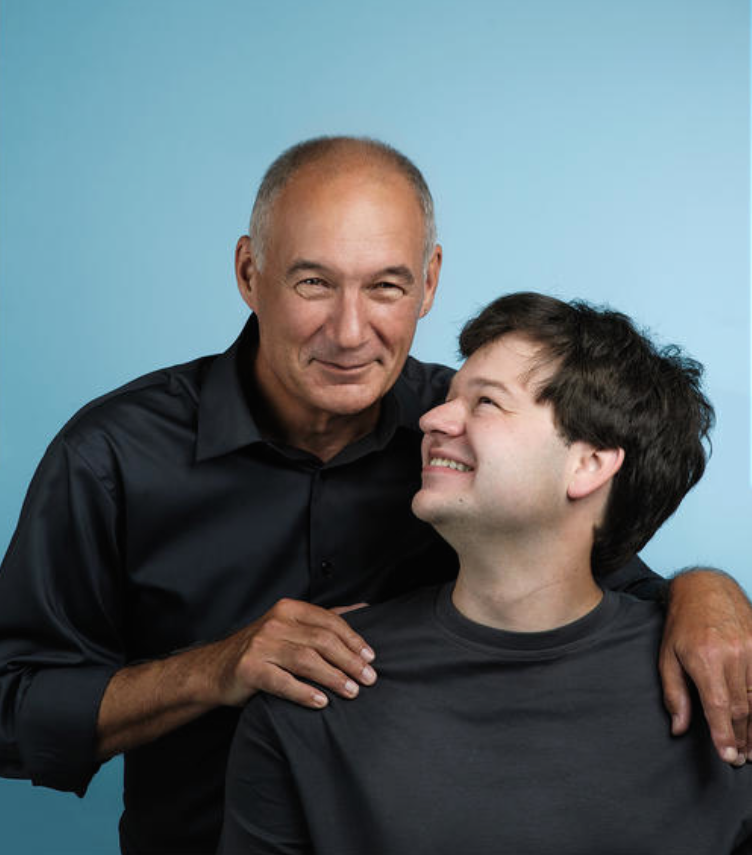
Mark Wafer (left) and Clint Sparling, an employee at one of his Tim Hortons locations
Mark Wafer, President of Megleen Treadstone and owner of several Tim Hortons coffee shop franchises, has transformed his businesses into much more than the routine place to enjoy caffeinated brew. Since opening his first franchise in 1995, Wafer designed his operations to be a proactive source of employment for people with disabilities. His success is now an established model that other businesses follow in doing the same.
Wafer’s first experience of hiring an employee with a disability was prompted by supply and demand. Having purchased his first franchise, he was confronted by a scarce labor market and so broadened his employee criteria. With that success and others like it, Wafer found that hiring people with disabilities is not simply a matter of altruism —it is good business. He has since founded SenseAbility to help other businesses learn the advantages of expanding hiring criteria to include people with disabilities.
Starting Out
Wafer and his wife launched their first franchise, Tim Hortons, in the early 90’s: “We liked the Tim Hortons franchise model and opportunities were available. We opened our first restaurant in East Toronto in 1995. We hired our first worker with a disability right away. We purchased an existing location with an already built clientele so we were very busy from day one. My staff however was all new and could not keep up so I had to hire someone to look after the dining room, dishes, tables and dishwasher and that’s how we discovered Clint Sparling.”
Sparling, who has Downs Syndrome, was Tim Hortons first inclusive hire. Wafer, who is Deaf, is especially aware of the barriers that many people with disabilities face in the job market. Extending this opportunity to Sparling made good business sense for both men. Wafer has made independence a possibility for Sparling and Sparling has been an invaluable employee. Now more two decades later, Sparling is still with Wafer’s Tim Hortons franchise. Wafer proudly reports “Clint has been with us for twenty-two years. He is married now and owns his own condo as a result of having a job and a paycheck.”
Good for Business
Within a few weeks of purchasing his first location, Wafer added a second. Throughout the process, he continued to hire employees with intellectual disabilities. Not long after, he began to take note of the economic benefits to him that resulted from his inclusive employment practice.
Wafer states, “The average annual employee turnover in the QSR business (Quick Service Restaurant) is about 100% and perhaps higher in high density areas. Mine is 40% or lower.”
He adds that the average tenure of a non-disabled worker in his franchises is one year and three months. However, his employees with disabilities stay on the job for an average of seven years. The importance of turnover can be measured in dollars and cents. According to Wafer, “an entry level worker costs about $4,000 to replace.” But, he also says that he discovered employing workers with disabilities not only reduced employee turnover but also increased productivity, innovation and safety. In addition to measurable, associated costs, there are other costs, which are not as easily quantifiable: “Once a person with a disability learns the task, they will only do it that way and not take shortcuts. They continue to do it the right way, time after time.”
Of course, these positive economic measures buoyed Wafer’s desire to continue his employment initiative: “As I began to see clear economic factors, lower absenteeism and higher productivity, I continued to hire workers with intellectual disabilities and decided to open our doors to workers with any sort of disability. As long as they could do the job, and if the training made sure they had whatever accommodation they might need, we hired them. ”
Since its first hire in 1995, Wafer’s franchises have employed over 150 people with disabilities in every aspect of the business including management: “Today, 46 or about seventeen percent of our 250 employees identify as having a disability in all six current locations. They are pretty much evenly distributed among my franchises.” (Wafer notes that the Tim Hortons chain does not have a franchise-wide policy on the employment of people with disabilities.)
Recruitment, Training and Hiring
The recruitment process, according to Wafer, is quite simple. “We are well-known in the community so candidates with disabilities apply often and are open about their situation. From the beginning, I set the tone for inclusion and my managers slowly bought into it. Today, when a manager interviews a non-disabled candidate, we ask how that person feels about working with people with disabilities. If we don’t get the right answer, that person does not get a second interview.”
Canadian Government’s Role
According to Wafer, the role of government is to lead by example and provide awareness. It is up to the business and corporate sectors to make change happen. “Canada”, he observes, “has little in the way of legislation that helps people with disabilities find work or that supports them when they do find work.” Wafer himself was appointed to a government panel in 2012 to find out why more businesses were not hiring workers with disabilities. He says, “The report resonated with corporations and the one take-away for the panel was that corporations wanted to hire more from this massive talent pool but really didn’t know what to do. So, the Canadian Federal Finance Minister provided money to establish the Canadian Business SenseAbility.”
“The idea for this association,” he explains, “came from my time on the panel exploring the success in the U.K. As part of my interviews with corporate leaders I became aware of a group known as the British Forum on Disability and it was their ideas and procedures that gave us the idea of starting SenseAbility. This is a membership driven association with the express purpose of creating disability confident companies. We work with the CEO and executive level, as well as HR and operational managers. Today, twenty-one corporations representing 800,000 employees are members of SenseAbility.” The organization provides these companies with an abundance of information that they select in order to make it easier for them to hire people with disabilities into their companies. Tim Hortons Corporate is a current member of SenseAbility. They, too, recognize the benefits Wafer I did. The real success with the brand however has been with other franchise owners across the country and the U.S. In Ontario alone there are 500 restaurants that have hired at least one worker with a disability.
Honors for Wafer
As the recipient of a variety of industry awards, Wafer’s work has been recognized for its value both to Canada and the Canadian economy. He observes, “In many areas of Canada we have a labor shortage that is only going to get worse. I suggest to restaurant owners in these areas to focus on the disability community for long term excellent employees. This is a new concept to them because they may currently view disability as a negative rather than a contributing factor to success. We’ve found that building awareness and educating business owners works.”
There are two sets of initials that follow Mark Wafer’s name: MSC and OMC. Awarded to Wafer by the Queen Elizabeth II in 2016, the MSC is the Meritorious Service Cross and is one of the highest awards for public service that can be given in Canada. The OMC, the Ontario Medal for Good Citizenship, is the second highest award in Ontario and was given to Wafer in March 2017. According to its website, “this medal recognizes individuals for their exceptional long-term efforts and outstanding contributions to the well-being of their communities.”
The Future
Moving forward, company-hiring credos must be: “Employable until proven otherwise.” Mark Wafer’s proves that this is a viable model: “In general we know that in five years we have found work for over a thousand people. This tells us that the message of inclusion for business is working. We don’t keep that data for the purpose of the numbers – we don’t want the numbers. Many of the projects we have initiated are based on the ‘business” model and how hiring impacts productivity, reduces absenteeism and turnover. Susan Scott Parker, CEO and creator of the British Forum on Disability, has worked on it with us and helped us to spread the word.”
He goes on to observe, “We have taken our model to other provinces and it is doing well there, too. We even went into the United States, to Syracuse and Rochester. When we tell them they are going to make more money by hiring people with disabilities, the message is heard! They go back and make it work with the result of a lot of people with disabilities finding work.”
Although Wafer does not like to measure with numbers, he says, “I worked on a project with the Ontario government that ended two years ago. We did some research on savings to government if a certain number of people with disabilities found jobs and figured out that including seasonal and even minimum wage jobs, the government saves $78 million annually with the employment of five thousand workers with disabilities.”
Wafer concludes with this: “One of the things I do is public speaking to explain the impact. The percent of people in Canada who have a disability may only be fifteen percent (roughly the same as in the U.S.) however, when you add in family members, the percent of the population rises to fifty-three percent! That number of people cannot be ignored.”
People with disabilities do not make up a niche market. They are the wives, husbands, sons, daughters, brothers, sisters and friends found in every community. Indeed, they are a massive market segment for the goods and services of those who hire people with disabilities. As Marc Wafer attests, not only are they a proven employee resource, they are extensions of the promising economic networks encompassing them.
 For over a century, the Ford Motor Company has distinguished itself as an innovator in automotive technology and design. With 67 plants worldwide, this industry giant commands a workforce of over 200,000 that will now expand to include persons on the autism spectrum as part of its groundbreaking program FordInclusiveWorks. While similar employment models are increasingly common throughout the business world, what distinguishes the Ford initiative is that positions will be offered at various levels throughout the company rather than in assembly lines alone
For over a century, the Ford Motor Company has distinguished itself as an innovator in automotive technology and design. With 67 plants worldwide, this industry giant commands a workforce of over 200,000 that will now expand to include persons on the autism spectrum as part of its groundbreaking program FordInclusiveWorks. While similar employment models are increasingly common throughout the business world, what distinguishes the Ford initiative is that positions will be offered at various levels throughout the company rather than in assembly lines alone Crucial to achieving those goals has been the partnership Ford built with
Crucial to achieving those goals has been the partnership Ford built with